📊 Statistics & Research on Screen Time Risks for Children
Share
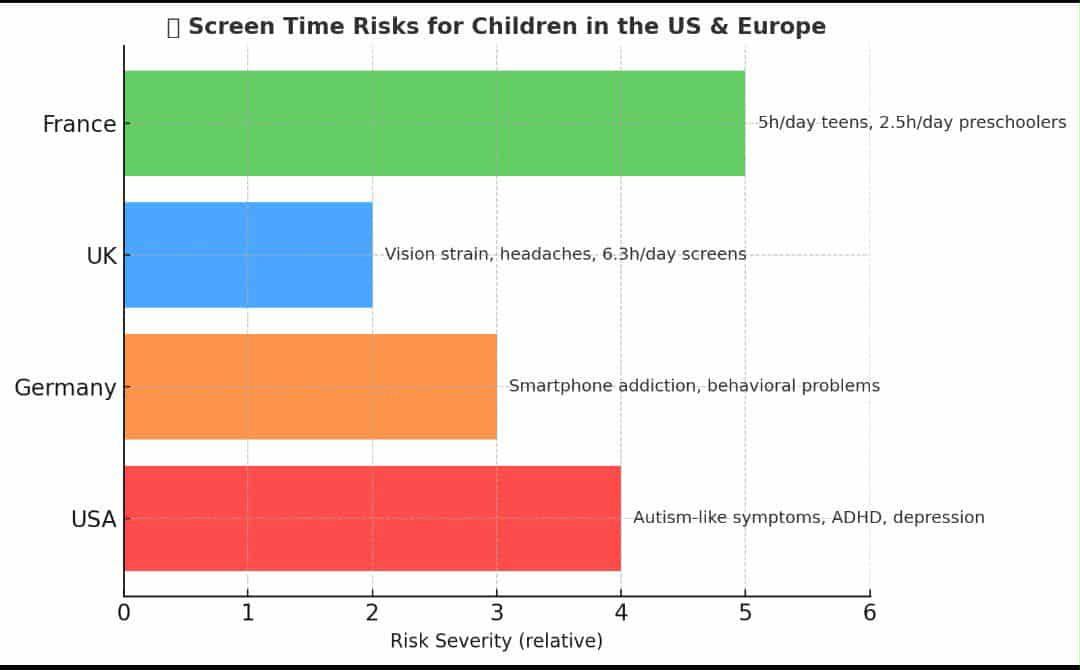
![]() United States 1. Mental Health & ADHD A U.S. study of 50,231 children aged 6–17 (National Survey of Children’s Health, 2020–2021) found that children spending 4+ hours per day on screens were significantly more likely to suffer from anxiety, depression, behavioral disorders, and ADHD. (Source: arxiv.org, 2025) 2. Autism-like Symptoms Research titled “The Association Between Screen Time Exposure and Autism Spectrum Disorder-Like Symptoms in Children” showed that children aged 4–6 who used screens for 3+ hours daily had a higher risk of autism-like symptoms compared to those using screens for 1 hour or less. (Source: PubMed, 2021) 3. Early Developmental Delays Children exposed to ≥3 hours of daily screen time before age 2 showed language delays, poor attention span, and hyperactivity compared to children with lower screen exposure. (Source: PubMed, 2018)
United States 1. Mental Health & ADHD A U.S. study of 50,231 children aged 6–17 (National Survey of Children’s Health, 2020–2021) found that children spending 4+ hours per day on screens were significantly more likely to suffer from anxiety, depression, behavioral disorders, and ADHD. (Source: arxiv.org, 2025) 2. Autism-like Symptoms Research titled “The Association Between Screen Time Exposure and Autism Spectrum Disorder-Like Symptoms in Children” showed that children aged 4–6 who used screens for 3+ hours daily had a higher risk of autism-like symptoms compared to those using screens for 1 hour or less. (Source: PubMed, 2021) 3. Early Developmental Delays Children exposed to ≥3 hours of daily screen time before age 2 showed language delays, poor attention span, and hyperactivity compared to children with lower screen exposure. (Source: PubMed, 2018) ![]() Germany 4. Problematic Smartphone Use A German study (BMC Psychiatry) on adolescents aged 12–19 found that problematic smartphone use (2+ hours daily or addiction-like symptoms) was linked to behavioral difficulties, lower quality of life, and worse academic performance. (Source: BMC Psychiatry, 2022) 5. Behavioral Problems Over Time A longitudinal German study (ages 10–16) revealed that teens who increased smartphone use or developed addictive patterns within one year showed greater externalizing behavior problems (e.g., disruptive conduct). (Source: PubMed, 2021)
Germany 4. Problematic Smartphone Use A German study (BMC Psychiatry) on adolescents aged 12–19 found that problematic smartphone use (2+ hours daily or addiction-like symptoms) was linked to behavioral difficulties, lower quality of life, and worse academic performance. (Source: BMC Psychiatry, 2022) 5. Behavioral Problems Over Time A longitudinal German study (ages 10–16) revealed that teens who increased smartphone use or developed addictive patterns within one year showed greater externalizing behavior problems (e.g., disruptive conduct). (Source: PubMed, 2021) ![]() United Kingdom 6. Vision Problems During Remote Learning Research from Anglia Ruskin University showed that switching between multiple digital devices (phone + computer) increased eye strain, temporary blurred vision, and unstable binocular vision in children. (Source: The Independent, 2022) 7. Daily Screen Hours UK reports show children aged 5–16 spend an average of 6.3 hours daily on screens (TV, tablets, gaming, smartphones), increasing the risk of headaches, blurred vision, and concentration problems. (Source: Specsavers UK, 2023)
United Kingdom 6. Vision Problems During Remote Learning Research from Anglia Ruskin University showed that switching between multiple digital devices (phone + computer) increased eye strain, temporary blurred vision, and unstable binocular vision in children. (Source: The Independent, 2022) 7. Daily Screen Hours UK reports show children aged 5–16 spend an average of 6.3 hours daily on screens (TV, tablets, gaming, smartphones), increasing the risk of headaches, blurred vision, and concentration problems. (Source: Specsavers UK, 2023) ![]() France 8. Teenagers’ Screen Use A French survey found that teens aged 13–19 spend over 5 hours daily on screens (internet, TV, gaming) — up from 4 hours 20 minutes a few years earlier. (Source: BFMTV, 2025) 9. Young Children’s Screen Exposure (<6 years) A study in Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes showed that children aged 2–4 already spend around 2.5 hours daily in front of screens, despite WHO recommendations for far less. (Source: Université Clermont Auvergne, 2023) 10. National Cohort Study (18,000 children) A French longitudinal study found average screen use of: 56 minutes/day at age 2 1h 20m/day at age 3.5 1h 34m/day at age 5.5 This far exceeds WHO recommendations for children under 5. (Source: Le Point, 2023)
France 8. Teenagers’ Screen Use A French survey found that teens aged 13–19 spend over 5 hours daily on screens (internet, TV, gaming) — up from 4 hours 20 minutes a few years earlier. (Source: BFMTV, 2025) 9. Young Children’s Screen Exposure (<6 years) A study in Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes showed that children aged 2–4 already spend around 2.5 hours daily in front of screens, despite WHO recommendations for far less. (Source: Université Clermont Auvergne, 2023) 10. National Cohort Study (18,000 children) A French longitudinal study found average screen use of: 56 minutes/day at age 2 1h 20m/day at age 3.5 1h 34m/day at age 5.5 This far exceeds WHO recommendations for children under 5. (Source: Le Point, 2023) ![]() Conclusion for Parents: Across the U.S. and Europe, excessive screen time has been linked to autism-like symptoms, vision loss, developmental delays, depression, and behavioral problems. These findings confirm that protecting children from digital overexposure is not optional — it’s a necessity
Conclusion for Parents: Across the U.S. and Europe, excessive screen time has been linked to autism-like symptoms, vision loss, developmental delays, depression, and behavioral problems. These findings confirm that protecting children from digital overexposure is not optional — it’s a necessity
